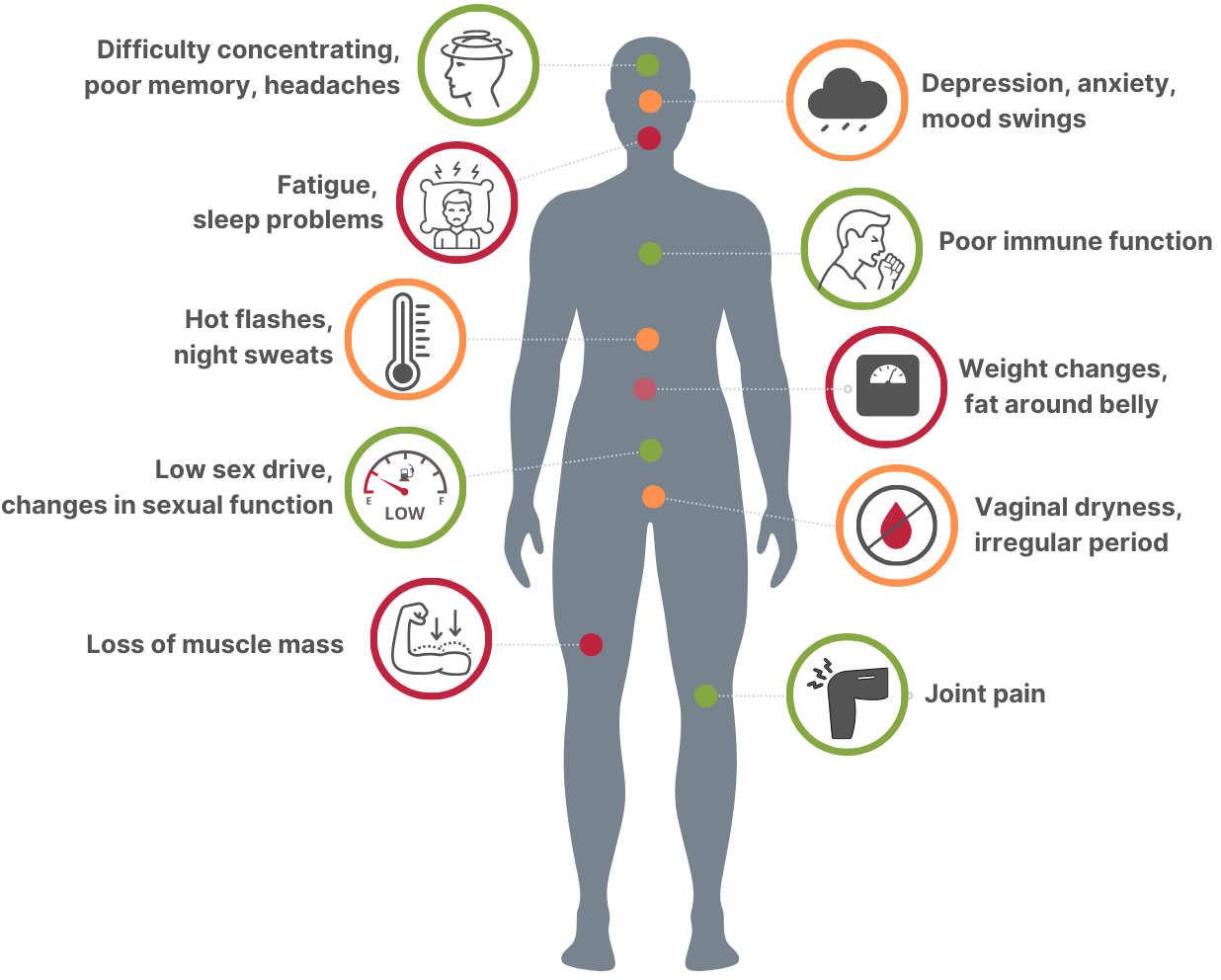
Symptoms Of Hormone Deficiency
Hormone Education
Educational Videos
Women
HRT: Everything You Need to Know – Dr. Peter Attia
Testosterone in Women: Benefits, Myths, and Realities
Men
TRT & Optimization – Dr. Peter Attia
Testosterone Replacement: Use Cases & Risks
PCOS
PCOS Explained: Pathophysiology, Symptoms, and Treatment
Understanding Your Hormone Therapy
Testosterone
General Info
Testosterone is the most abundant hormone in both men and women and plays a key role in energy, libido, bone health, muscle mass, and mood. Optimization improves quality of life and longevity.
Benefits
Energy, libido, muscle strength, metabolism, cognition, heart and bone protection, mood, and fat reduction.
Low T Risks
Heart disease, obesity, Type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s, osteoporosis, and metabolic syndrome.
Administration
Injections (IM or subq), creams (scrotal or labial), troches, oral capsules (women only).
Side Effects
Testicular atrophy, infertility, acne, fluid retention, increased RBCs. Most are dose-dependent and reversible.
Precautions
Avoid in active prostate cancer, pregnancy, breastfeeding. Use caution with clotting disorders, untreated OSA, or recent stroke.
Thyroid
General Info
Thyroid hormone controls metabolism, temperature regulation, heart rate, cognition, ovulation, and more.
Common Dysfunction Causes
Low T4, poor T4 → T3 conversion, receptor resistance (often missed by traditional treatment).
Benefits
Improves energy, metabolism, cognition, fertility, mood, fat burning, and blood sugar regulation.
Symptoms of Poor Function
Fatigue, cold intolerance, hair loss, constipation, high cholesterol, menstrual issues.
Administration
Oral T4+T3 combo, usually dosed 1–2x daily on an empty stomach.
Side Effects
Palpitations, sweating, anxiety — usually from overmedication or untreated hyperthyroidism.
Estrogen
General Info
Estradiol is the primary, most active estrogen. We use only bioidentical forms—not synthetic Premarin.
Benefits
Cardiovascular, bone, brain, vaginal, bladder, skin, mood, and metabolic health. Reduces all-cause mortality.
Low Estradiol Signs
Mood swings, hot flashes, fatigue, insomnia, vaginal dryness, painful sex, memory issues.
Administration
Oral (most effective), cream, vaginal troche, or patch (less reliable). Route depends on clotting history.
Side Effects
Breast tenderness, spotting, fluid retention (adjust dose or add progesterone).
Precautions
Avoid oral estradiol with a DVT/clotting history; use cream or troche instead.
Progesterone
General Info
Works synergistically with estrogen. Imbalances can cause PMS, mood changes, fluid retention, and cancer risks.
Benefits
Protects brain, bone, breast, uterus. Improves sleep, mood, metabolism, and balances estrogen.
Deficiency Symptoms
PMS, insomnia, depression, anxiety, spotting, fibroids, migraines, weight gain.
Administration
Oral capsules (bioidentical), typically at night to enhance sleep and circadian rhythm.
DHEA
General Info
An adrenal steroid that acts as a precursor to testosterone, estrogen, and progesterone. Supports immune, metabolic, and mood health.
Benefits
Energy, lean mass, fat loss, blood sugar control, cognition, immune support, and cortisol balance.
Administration
Oral capsules in the morning or midday, taken with food (fat-soluble).
Precautions
Avoid in pregnancy, active cancer, recent stroke, or clotting history. Monitor blood levels.
Side Effects
Acne, hair growth (mitigated by dose adjustment).
